By the end of the dry season, the water trails of the Ceriso are worn to a white ribbon in the leaning grass, spread out faint and fanwise toward the homes of gopher and ground rat and squirrel.
But however faint to man-sight, they are sufficiently plain to the furred and feathered folk who travel them. Getting down to the eye level of rat- and squirrel-kind, one perceives what might easily be wide and winding roads to us if they occurred in thick plantations of trees three times the height of a man. It needs but a slender thread of barrenness to make a mouse trail in the forest of the sod. To the little people, the water trails are as country roads, with scents as signboards.
There is little water in the Ceriso at the best of times, and that little brackish and smelling vilely, but by a lone juniper where the rim of the Ceriso breaks away to the lower country, there is a perpetual rill of fresh, sweet drink in the midst of lush grass and watercress. In the dry season there is no water else for a man’s long journey of a day. East to the foot of Black Mountain, and north and south without counting, are the burrows of small rodents, rat- and squirrel-kind. Under the sage are the shallow forms of the jackrabbits, and in the dry banks of washes, and among the strewn fragments of black rock, lairs of bobcat, fox, and coyote.
The coyote is your true water witch, one who snuffs and paws, snuffs and paws again at the smallest spot of moisture-scented earth until he has freed the blind water from the soil. Many water holes are no more than this detected by the lean hobo of the hills in localities where not even an Indian would look for it.
It is the opinion of many wise and busy people that the hill folk pass the ten-month interval between the end and renewal of winter rains with no drink; but your true idler, with days and nights to spend beside the water trails, will not subscribe to it. The trails begin, as I said, very far back in the Ceriso, faintly, and converge in one span broad, white, hard-trodden way in the gully of the spring. And why trails if there are no travelers in that direction?
I have yet to find the land not scarred by the thin, far roadways of rabbits and whatnot of furry folks that run in them. Venture to look for some seldom-touched water hole, and so long as the trails run with your general direction, make sure you are right, but if they begin to cross yours at never so slight an angle, to converge toward a point left or right of your objective, no matter what the maps say, or your memory, trust them; they know.
It is very still in the Ceriso by day, so that were it not for the evidence of those white beaten ways, it might be the desert it looks. The sun is hot in the dry season, and the days are filled with the glare of it. Now and again some unseen coyote signals his pack in a long-drawn, dolorous whine that comes from no determinate point, but nothing stirs much before midafternoon. It is a sign when there begin to be hawks skimming above the sage that the little people are going about their business.
The coyotes that are astir in the Ceriso of late afternoons, harrying the rabbits from their shallow forms, and the hawks that sweep and swing above them, are not there from any mechanical promptings of instinct but because they know of old experience that the small fry are about to take to seed gathering and the water trails. The rabbits begin it, taking the trail with long, light leaps, one eye and ear cocked to the hills from whence a coyote might descend upon them at any moment. Rabbits are a foolish people. They do not fight except with their own kind, nor use their paws except for feet, and appear to have no reason for existence but to furnish meals for meat eaters. In flight they seem to rebound from the earth of their own elasticity but keep a sober pace going to the spring. It is the young watercress that tempts them and the pleasures of society, for they seldom drink. Even in localities where there are flowing streams, they seem to prefer the moisture that collects on herbage, and after rains may be seen rising on their haunches to drink delicately the clear drops caught in the tops of the young sage. But drink they must, as I have often seen them mornings and evenings at the rill that goes by my door. Wait long enough at the Lone Tree Spring and sooner or later they will all come in.
The crested quail that troop in the Ceriso are the happiest frequenters of the water trails. There is no furtiveness about their morning drink. About the time the burrowers and all that feed upon them are addressing themselves to sleep, great flocks pour down the trails with that peculiar melting motion of moving quail, twittering, shoving, and shouldering. They splatter into the shallows, drink daintily, shake out small showers over their perfect coats, and melt away again into the scrub, preening and pranking, with soft contented noises.
After the quail, sparrows and ground-inhabiting birds bathe with the utmost frankness and a great deal of splutter; and here, in the heart of noon, hawks resort, sitting panting, with wings aslant, and a truce to all hostilities because of the heat. One summer there came a roadrunner up from the lower valley, peeking and prying, and he had never any patience with the water baths of the sparrows. His own ablutions were performed in the clean, hopeful dust of the chaparral; and whenever he happened on their morning splatterings, he would depress his glossy crest, slant his shining tail to the level of his body, until he looked most like some bright venomous snake, daunting them with shrill abuse and feint of battle. Then suddenly he would go tilting and balancing down the gully in fine disdain, only to return in a day or two to make sure the foolish bodies were still at it.
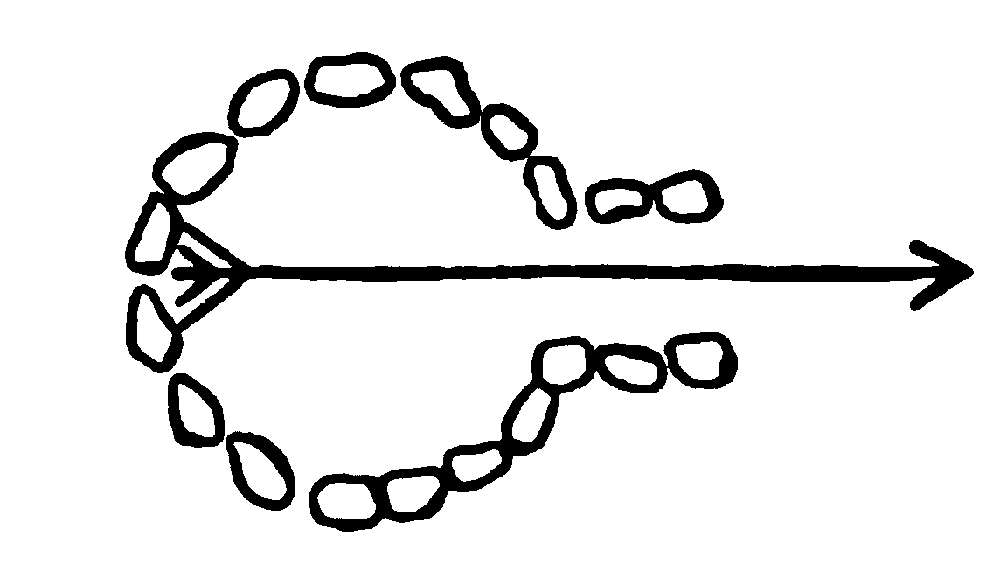
Out on the Ceriso about five miles, and wholly out of sight of it, near where the immemorial foot trail goes up from Saline Flat toward Black Mountain, is a water sign worth turning out of the trail to see. It is a laid circle of stones large enough not to be disturbed by any ordinary hap, with an opening flanked by two parallel rows of similar stones, between which, were an arrow placed touching the opposite rim of the circle, it would point as the crow flies to the spring. It is the old, indubitable watermark of the Shoshones. One still finds it in the desert ranges in Salt Wells and Mesquite valleys, and along the slopes of Waban. On the other side of Ceriso, where the black rock begins, about a mile from the spring, is the work of an older, forgotten people. The rock hereabout is all volcanic, fracturing with a crystalline whitish surface, but weathered outside to furnace blackness.
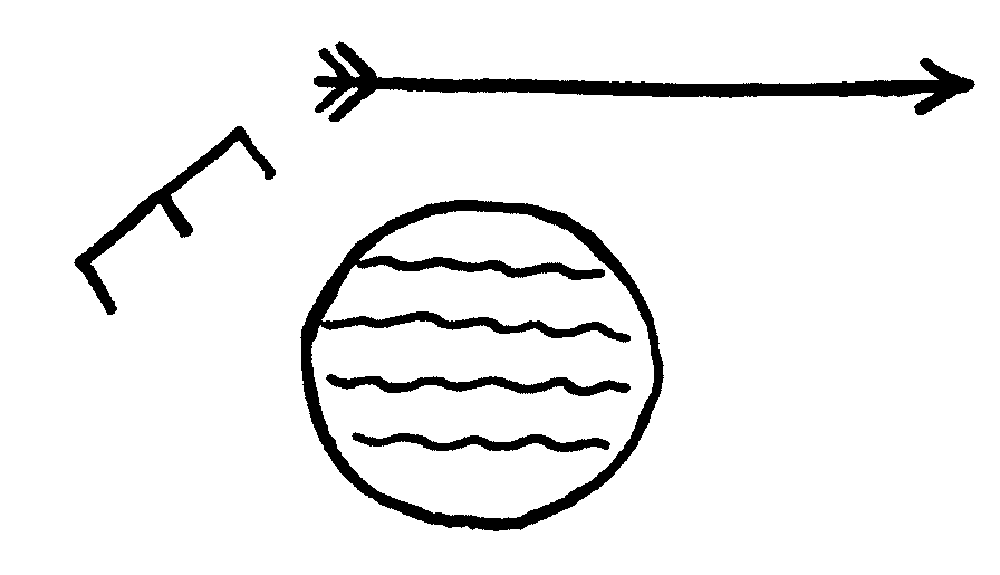

Around the spring, where must have been a gathering place of the tribes, it is scored over with strange pictures and symbols that have no meaning to the Indians of the present day; but out where the rock begins, there is carved into the white heart of it a pointing arrow over the symbol for distance and a circle full of wavy lines reading thus: “In this direction three [units of measurement unknown] is a spring of sweet water; look for it.”
From The Land of Little Rain. After moving to California on her graduation from Blackburn College in 1888, Austin developed an affinity for the desert area of Owens Valley. “The real heart and core of the country are not to be come at in a month’s vacation,” she writes in the preface to this, her first book. “One must summer and winter with the land and wait its occasions.” An active Fabian socialist, Austin died in 1934 in Santa Fe.
Back to Issue



