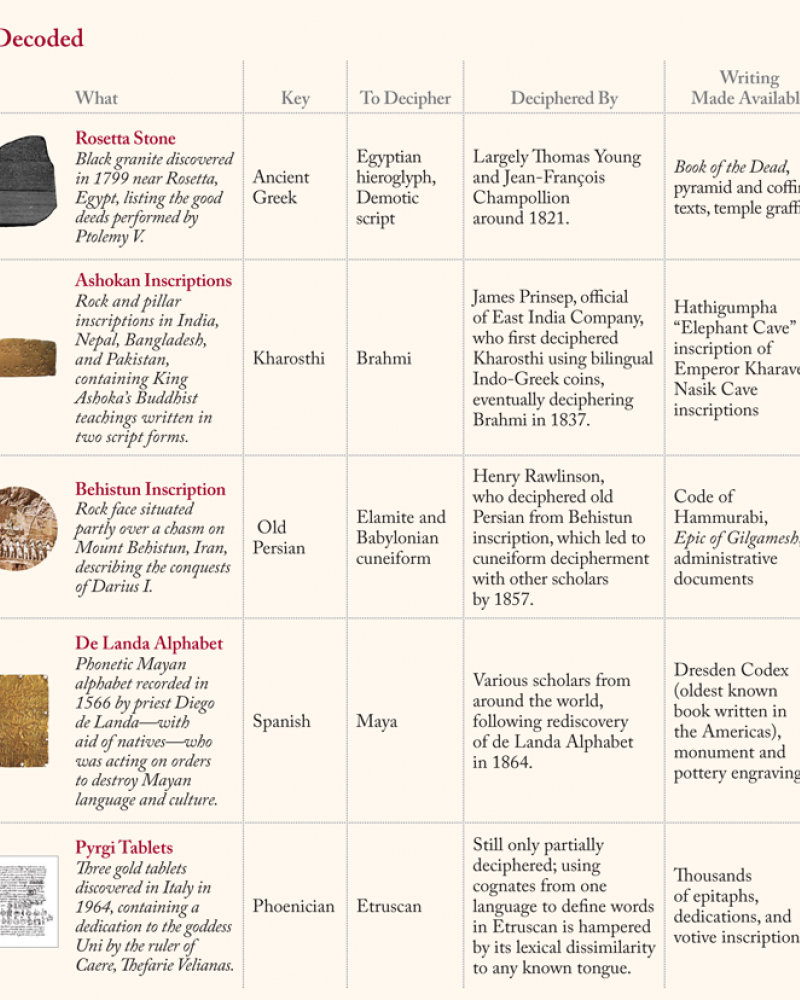
Miscellany
It is said that Alexander the Great once found Diogenes the Cynic examining a pile of human bones. “What are you looking for?” the ruler inquired. “I am searching for the bones of your father,” replied the philosopher, “but I cannot distinguish them from those of his slaves.” On another occasion a woman came to see Diogenes, complaining that her son was poorly behaved, and asked what she could do about it. Diogenes answered by slapping the woman in the face.